Sarkari Yojana, sarkari yojana 2023, sarkari yojana.com up, गाँव संबंधी सरकारी योजनाओं की जानकारी, government schemes list, मुख्यमंत्री की सभी योजनाएं, sarkari yojana.com csc, sarkari yojana 2023 up, sarkari yojana.com bihar, Sarkari yojana 2022
Sarkari Yojana: The Indian government is committed to the well-being of society and regularly introduces diverse welfare schemes to address the needs of different population groups. These schemes operate at central, state, or joint levels, showcasing a comprehensive strategy to enhance citizens’ lives.

Our aim is to make information about government welfare schemes easily accessible. We want to create a user-friendly hub where you can effortlessly find details about numerous schemes.
This includes information about who qualifies for benefits, the types of benefits offered, scheme intricacies, and other crucial details for a complete understanding.
Our easy-to-read format consolidates this information, empowering individuals with the knowledge needed to access the benefits provided by these schemes. This centralized access serves as a valuable resource.
Promoting transparency and awareness about the government’s commitment to socio-economic development and the well-being of all segments of society. Explore this section to stay informed and make the most of the various welfare opportunities offered by the Government of India.
Sarkari Yojana
“Sarkari Yojana” is your easy-to-use online platform, providing accessible and abundant information about various government initiatives. Explore the world of Sarkari Yojnaa and PM Modi Yojana 2023—the ultimate online hub that simplifies connecting with government schemes and offers detailed information.

Dive into the details of government schemes guided by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chief Ministers on the user-friendly Sarkari Yojana website. Understand each scheme thoroughly, including its objectives, eligibility criteria, benefits, and the application process.
Our platform serves as a one-stop destination, keeping you updated on the latest developments in government initiatives. Effortlessly navigate the website to access a wealth of details, ensuring a complete understanding of each scheme’s nuances.
Stay connected and make informed decisions using the Sarkari Yojana platform as your gateway to the expansive world of government schemes and welfare programs. Take full advantage of this invaluable resource to enhance your understanding and actively participate in the transformative initiatives envisioned by the Government of India.
What are the Schemes for the poor?
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana
- Pm Mudra yojna
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
- Atal Pension Yojana
- Jawahar Gram Samridhi Yojana
- National Social assistance Programme
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
- Ayushman Bharat Yojana
- Indira Gandhi National Disabled Pension Scheme
- Mission Antyodaya
- National Rural Livilihood Mission
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- Integrated Rural Development Programme
- Jawahar Rozgar Yojana
- National Urban Livelihood Mission
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana
- National Food For Work Programme
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana
- Annapurna
- Deen Dayal Sparsh Yojana
- Disability Pension Scheme
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Mandhan Yojana
- Chief Minister Girls Marriage Scheme
- Cm Disabled Marriage Incentive Scheme
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana
What Projects are Currently Running?
- Bharatmala Pariyojana
- Narmada Valley Development Project
- Chenab River Railway Bridge
- Delhi Metro Industrial Corridor
- Mumbai Trans Harbour Link
- Inland WaterWays Development Project
- Navi Mumbai International Project
- Zoji-la and Z-Morh Tunnel Project
[su_button url=”https://epi.gov.in/content/innerpage/major-current-project.php” target=”blank” style=”flat” background=”#b60e11″ size=”7″ center=”yes” radius=”round”]MAJOR CURRENT PROJECTS[/su_button]
List of Top Future Megaprojects in India 2023
Bullet Train:
The National High-Speed Rail Corporation (NHSRCL) is making strides in bringing India’s first bullet train project to reality, connecting Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
Initial expectations for the project to begin in April 2020 faced construction delays, but recent reports are optimistic, indicating the project is on track for completion by December 2023.
The project spans a vast 352 km stretch between Mumbai and Gujarat, with plans for operational readiness by 2027. A significant milestone is expected by 2026, as a crucial 50-kilometer stretch between Surat and Bilimora is slated for completion.
This high-speed rail initiative signifies a major advancement in India’s transportation infrastructure, promising enhanced connectivity, shorter travel times, and a substantial boost to regional development.
As anticipation grows for the realization of this modern transportation marvel, the ongoing progress and milestones in the construction process highlight advancements in India’s high-speed rail travel landscape.
Central Vista:
The Central Vista Redevelopment Project is a continuous and transformative initiative happening at the core of India’s administrative hub, Central Vista, on New Delhi’s iconic Raisina Hill.
This ambitious effort, integral to the Aatma Nirbhar Bharat vision, aims to revamp and redevelop existing infrastructure for long-term sustainability while preserving the historical significance of heritage buildings and enhancing public spaces.
At its core, the project envisions a holistic transformation, not just in terms of physical structures but also in creating an environment that fosters efficiency, accessibility, and modernity in administrative functions.
The careful planning and execution of this redevelopment align with the principles of self-reliance, laying the foundation for a vibrant and forward-looking administrative precinct.
In the ongoing Central Vista Redevelopment Project, the focus extends beyond architectural enhancements. It aims to create a dynamic and efficient administrative space catering to the evolving needs of governance while emphasizing the preservation of heritage structures emblematic of India’s rich history.
The project serves as a testament to the commitment to both modernization and heritage conservation, contributing to the overall development and identity of New Delhi as the capital city of India.
Bharatmala:
Adding to the Central Vista Redevelopment Project, there’s another significant initiative in India that demands attention—the Bharatmala project. This extensive effort strategically focuses on developing a comprehensive infrastructure network, including tunnels, roadways, elevated corridors, flyovers.
Interchanges, bypasses, overpasses, and more. Its primary objective is to enhance the efficiency of the National Corridor in India, covering essential routes like the Golden Quadrilateral and the North-South-East-West corridors.
The Bharatmala project is a pivotal driver of India’s infrastructural growth, set to reshape the transportation landscape nationwide. With a dedicated emphasis on improving connectivity and streamlining transportation systems, it promises to facilitate smoother and more efficient movement of goods and people.
As per recent reports, Phase-I of the Bharatmala project is expected to wrap up by the end of 2026, marking a significant milestone in its overall timeline.
Underscoring the scale and importance of the project, the estimated cost has now surged to a substantial INR 8.5 lakh crore, highlighting the commitment to comprehensive and transformative infrastructural development in India.
Sagarmala:
In India’s major infrastructure initiatives, the Sagarmala project takes a significant position under the leadership of the Government of India.
This ambitious endeavor is all about improving logistics efficiency across the country, placing a key emphasis on optimizing India’s extensive waterways and coastline. The primary aim is to usher in a new era of maritime connectivity and development.
The Sagarmala project focuses on making direct and indirect port-based development more efficient, ensuring a smooth transport of goods between ports by eliminating bottlenecks.
By harnessing the vast potential of water-based transport, the initiative seeks to redefine maritime logistics, enhancing connectivity, and promoting economic activities along the coastline.
Aligned with the broader goal of creating an integrated and efficient maritime infrastructure network, the Sagarmala project not only promises to enhance economic activities but also to significantly contribute to advancing India’s logistics capabilities.
As the project progresses, it is expected to play a pivotal role in the country’s growth trajectory, leaving a lasting impact on India’s development landscape.
Dedicated Freight Corridors:
For those not familiar with the concept, dedicated freight corridors in India are essentially specialized networks of broad gauge freight railway lines exclusively reserved for the operations of freight trains and their services.
This mega project plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency and expediting the entire process of freight transportation.
The integration of dedicated freight corridors simplifies the functions of freight trains, ensuring a smoother, faster, and more effortless movement of goods. By designating these corridors specifically for freight traffic, it alleviates congestion on existing railway lines, which are often shared between passenger and freight services.
India’s dedicated freight corridors are organized into six major sections, each serving a distinct geographical region and contributing to the seamless flow of goods.
These sections include the Western Dedicated Freight Corridor, Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor, East-West Dedicated Freight Corridor, North-South Dedicated Freight Corridor, East Coast Dedicated Freight Corridor, and Southern Dedicated Freight Corridor.
This strategic division caters to the unique logistical needs of different regions, promoting economic growth and fortifying the country’s transportation infrastructure.
The dedicated freight corridors embody a forward-looking approach to meeting the increasing demands of freight transportation, prioritizing efficiency, speed, and reliability in the movement of goods across India’s diverse landscapes.
Delhi-Mumbai Expressway:
The Delhi-Mumbai highway is a 1350 km long, eight-lane, access-controlled highway that is currently under construction. The nation’s financial center, Mumbai, and the capital city, Delhi, will be connected by this expressway. On March 8, 2019, this project was officially launched.
It is anticipated that the journey duration will decrease from 24 hours to 12 hours with the availability of the 8-lane division in the expressway. Moreover, after the highway is operational, space for an extra four lanes would be set aside for future growth.
One of India’s most ambitious upcoming megaprojects that would affect the country’s economic development is this one.
Chenab Railway Bridge:
Constructed around 358 meters above sea level, the Chenab Railway Bridge has the title of highest rail bridge in the world. The bridge spans 42 kilometers between Bakkal and Kauri and spans the Chenab River. It is an arch bridge composed of steel and concrete.
The bridge’s base support was finished in November 2017, and the full structure was finished and opened in August 2022. This bridge is 1315 meters long and has a deck height of 359 meters.
The Northern Railway took on the project. The bridge is shaped like an arch and has two ribs made of big steel trusses.
5G:
The official launch of 5G services in India took place on October 01, 2022, under the leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi.
Networks like Airtel and Jio have already released their 5G services and made it available to their subscribers for continued use. The same was announced during the India Mobile Congress.
The availability and integration of the same will facilitate networking and communication throughout the entire process, particularly in India’s rural areas where communication problems are common. India is currently in the process of becoming heavily digitalized.
DMIC – Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor:
The Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor, also known as DMIC, was the first industrial corridor planned to connect Delhi and Mumbai, the two largest cities in India, as part of the Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC).
The same would cross several important states before arriving in Maharashtra, including Uttar Pradesh, Delhi NCR, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
Although the DMIC is still under development, projections indicate that the project will likely cost a total of about $90 billion.
The project is registered with the Government of India owning 49% of the equity, JBIC (Japan Bank for International Cooperation) owning 29%, and other government entities owning the remaining portion.
Dholera Smart City:
Currently under construction in Gujarat, the Dholera Smart City is the nation’s newest and most advanced smart city. It is anticipated to build a futuristic, sustainable, and livable environment for India’s current and future generations.
The project’s main goal is to create a city where residents’ quality of life is prioritized. The distance between the city and Ahmedabad is about 40 kilometers. The project is still being built, having begun in 2005.
The Indian government intends to use this initiative to give future people access to essential utilities, sustainable living conditions, and inexpensive housing.
Aditya L1 mission:
According to sources, India’s first space mission to study the Sun, the Aditya L1 mission, is expected to launch by June or July. Launched to the L1 orbit, the mission’s goal is to continuously observe the Sun and learn more about the surrounding atmosphere.
According to reports, the Indian Institute of Astrophysics in Bengaluru designed the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), which is the primary payload of the Aditya L1. The spacecraft is now carrying seven payloads total. Understanding how the Sun affects Earth is the main goal of this project.
Gaganyaan Mission:
ISRO’s next human spaceflight project, called the Gaganyaan Mission, is scheduled to launch at least three astronauts into space and keep them there for about seven days. Covid-19’s onset caused an initial delay in the mission.
The primary objective is to launch the astronauts into a 400 km orbit and safely return them to Earth by landing in the Indian Ocean. According to Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for Space, the mission is scheduled for the fourth quarter of 2024.
Defence Industrial Corridor:
The Indian government has established and proposed the Defence Industrial Corridor as a way to lessen reliance on India’s aerospace and defense industry from outside.
India is home to several defense corridors, such as the Uttar Pradesh Defence Industrial Corridor, which has six nodal points: Lucknow, Agra, Aligarh, Chitrakoot, Jhansi, and Kanpur. The Tamil Nadu Defence Corridor, which encompasses Tiruchirappalli, Hosur, Salem, Chennai, and Coimbatore, is also included.
Indian Space Station:
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is a space station that the Indian government plans to build and expand. The space station is expected to weigh twenty tons and fly 400 kilometers above Earth in an orbit.
In the future, when ISRO conducts human spacecraft flights, astronauts will be able to spend 15 to 20 days staying here.
Great Nicobar Development:
The Great Nicobar development is a massive project that will be built out along Great Nicobar Island’s shoreline. According to reports, this development project aims to foster the growth of the region and the nation at large by building an international airport and aero-city housing.
It is anticipated that the project’s development will boost local tourism, which will further boost the nation’s economy. This is the most ambitious of India’s upcoming megaprojects that would affect the country’s overall expansion in the Bay of Bengal.
Here are a few of the megaprojects in India that are highly suggested that you be aware of. We hope you now know everything there is to know about the massive developments taking place in this rapidly changing country, India.
What are the government schemes for women?
- Working Women Hostel
- Pradhan Mantri Mahila Shakti Kendra
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao scheme
- Swadhar Greh
- Women Helpline Scheme
- One Stop Centre Scheme
- Scheme for Adolescent girls
- Chiranjeevi Yojana
- Balika Samridhhi Yojana
- Mahila Police Volunteers
- Pradhan Mantri Matritva Vandana Yojana
- Pradhan Mantri Rozgar Yojana
- Rajiv Gandhi National Creche Scheme
- Ujjawala scheme
- Mahila Coir Yojana
- Bharatiya Mahila Bank Business Loan
- Cent Kalyani Scheme
- Child Protection services Scheme
- Dena Shakti Scheme
- Nari Shakti Puraskar
- Poshan Abhiyaan
- STEP
- Udyogini Scheme
Central Government Schemes for Girl Child
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
- Balika Samridhi Yojana
- CBSE Udaan Scheme
- National Scheme of Incentive to Girls for Secondary Education
State Government Initiatives for Girl Child
- Mukhyamantri Kanya Suraksha Yojana
- Ladli Lakshmi Yojana
- Delhi Ladli Scheme
- Mukhyamantri Rajshri Yojana
- Mazi kanya Bhagyashree Scheme
- Tamil Nadu Chief Minister’s Girl Child Protection Scheme
- Nanda Devi Kanya Yojana
What is the Prime Minister’s new plan in 2023?
On August 16, 2023, the Union Cabinet of India showcased its commitment to traditional artisans and craftsmen by approving the implementation of the “PM Vishwakarma Yojana” nationwide.
This strategic decision reflects the government’s dedication to preserving and uplifting the rich heritage of traditional craftsmanship, recognizing the vital role played by artisans in India’s cultural and economic tapestry.
The introduction of this scheme is set to bring positive transformations, fostering the growth and sustainability of traditional arts and crafts. It aims to provide tangible support and opportunities for skilled artisans who contribute significantly to India’s cultural legacy.
The “PM Vishwakarma Yojana” stands as a testament to the government’s proactive approach in empowering and promoting the well-being of traditional craftsmen, ensuring the continued vibrancy and resilience of India’s diverse artisanal traditions.
What is the plan for the poor in 2023?
The Union Cabinet’s decision on December 23, 2022, to provide “free foodgrains to about 81.35 crore beneficiaries” starting January 1, 2023, under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) of 2013 is a significant move addressing the nutritional needs of the population.

This initiative emphasizes the government’s commitment to ensuring food security for a substantial section of the population, with approximately 813.5 million individuals identified as beneficiaries in need of assistance.
By extending this support, the government aims to alleviate economic challenges faced by a vast number of citizens, recognizing the importance of securing basic nutritional requirements for a considerable portion of the population.
This decision not only highlights the government’s responsiveness to the socio-economic needs of the people but also reflects a comprehensive approach to address food security issues across the nation.
The provision of free foodgrains for a year serves as a crucial intervention to bolster the well-being of a significant segment of the population, marking a pivotal step towards inclusive and sustainable development.
How much loan can a poor man get?
The Differential Rate of Interest (DRI) Scheme stands out as a crucial initiative dedicated to promoting financial inclusion and empowerment, with banks taking a central role in its implementation.
This scheme is tailored to offer essential support to the weaker sections of the community, providing financial assistance of up to ₹15,000 at a concessional interest rate of 4 percent per annum.
The primary objective of the DRI Scheme is to empower individuals from vulnerable sections, enabling their participation in productive and gainful activities.
By addressing economic disparities, the scheme strategically acts as a tool to extend a financial lifeline to those facing challenges accessing traditional banking services.
The concessional interest rates not only facilitate financial assistance but also act as an incentive for active participation in productive endeavors, contributing to overall community development and economic upliftment.
In alignment with broader socio-economic development goals, banks participating in the DRI Scheme recognize the transformative impact that targeted financial assistance can have on individuals and communities.
The scheme’s concessional interest rates serve as a catalyst, motivating individuals from marginalized sections of society to embark on ventures that enhance their economic well-being, fostering a more equitable and prosperous society.
What is the Subsidy Scheme?
The Differential Rate of Interest (DRI) Scheme is crafted as a credit-linked initiative with a distinct focus on projects centered around technology upgradation. To be eligible for benefits under this scheme, projects must align with the prescribed limit of term loans sanctioned by lending agencies.

It’s important to note that second-hand machinery does not qualify for consideration under this scheme.
The credit-linked framework ensures that the advantages of the scheme are channeled specifically towards projects striving to enhance technological capabilities. The set limit for term loans serves as a criterion for determining eligibility under the DRI Scheme.
The exclusion of second-hand machinery underscores the scheme’s commitment to promoting advancements and modernization in technology.
By maintaining a credit-linked structure and clearly defining criteria for eligibility, the DRI Scheme aims to efficiently direct its benefits to projects that align with the overarching goal of fostering technological progress in supported sectors.
This focused approach guarantees that the scheme significantly contributes to the growth and development of industries by encouraging initiatives for technology upgradation.
What are Modi’s plans?
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi took a significant step towards promoting skilled craftsmanship and traditional arts by officially launching the Central Sector Scheme PM Vishwakarma in New Delhi today.
This marks a pivotal move to empower artisans and craftsmen across the country, recognizing their vital contribution to India’s rich cultural heritage.
Simultaneously, events are being organized at approximately seventy locations across different parts of the country on the same day. These serve as platforms to raise wider awareness among potential beneficiaries, ensuring that the benefits of the PM Vishwakarma Scheme reach every corner of the nation.
By launching the scheme at a national level and organizing events in multiple locations, the government aims to actively engage with and empower traditional artisans, fostering sustainable growth in the traditional arts and crafts sector.
This initiative not only highlights the government’s commitment to preserving and promoting traditional craftsmanship but also emphasizes the importance of creating widespread awareness to maximize the scheme’s impact.
The launch event and associated awareness programs symbolize a concerted effort to revive and rejuvenate traditional arts, ensuring their continued vibrancy and relevance in the modern era.
What is the scheme for the youth?
The National Programme for Youth and Adolescent Development (NPYAD), led by the Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan (NYKS) under the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, is a pivotal initiative designed to address the diverse needs and aspirations of the youth and adolescents in the country.
As an integral part of the NPYAD Scheme, NYKS assumes a crucial role in channeling resources and support to empower young individuals, fostering their holistic development.
Under the aegis of the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, the NPYAD Scheme aims to establish a comprehensive framework to cater to the varied requirements of youth and adolescents.
The scheme encompasses a variety of programs and activities with a focus on fostering skill development, nurturing leadership qualities, and enhancing overall well-being among the target demographic.
NYKS, as the implementing body, plays a central role in executing the NPYAD Scheme at the grassroots level, ensuring that the benefits and opportunities reach youth and adolescents across the nation.
The collaborative efforts between NYKS and the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports underline the government’s unwavering commitment to nurturing the potential of the younger generation and contributing to their comprehensive growth and development.
Through the NPYAD Scheme, NYKS aims to create a supportive and empowering environment for youth and adolescents, facilitating their active participation in society and meaningful contributions to the nation’s progress.
This initiative reflects the government’s dedication to shaping a brighter future for the youth, laying the foundation for a dynamic and resilient generation.
Which is the most important scheme for rural employment?
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) is a landmark legislation enacted by the Government of India in September 2005.
This transformative Act was introduced with the primary objective of providing a legal guarantee of a hundred days of wage employment in a financial year to adult members of rural households.
The Act specifically targets individuals who demand employment and are willing to engage in unskilled manual work.
MGNREGA, rooted in the principles of social justice and rural development, has had a profound impact on the socio-economic landscape of rural India.
By offering a legal guarantee of employment, the Act seeks to address issues of unemployment and underemployment in rural areas, empowering individuals and communities to secure a livelihood and improve their economic well-being.
This groundbreaking initiative not only provides financial support to rural households but also aims to enhance overall economic stability, promote inclusive growth, and mitigate the challenges associated with seasonal unemployment in rural regions.
MGNREGA stands as a testament to the government’s commitment to fostering rural development, alleviating poverty, and ensuring social and economic equity in the country.
The Act has been instrumental in creating a positive impact on the lives of millions of rural citizens, embodying the spirit of Mahatma Gandhi’s vision for a self-reliant and empowered rural India.
What steps has the Indian government taken to end poverty in the country?
The Government of India is actively pursuing a comprehensive approach to combat poverty through impactful initiatives geared towards achieving holistic and sustainable development.
Key projects in this pursuit include the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 (MGNREGA), Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY), Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana (PMGY), and Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana (PMRY).
These initiatives are strategically designed to address various dimensions of poverty and upliftment, emphasizing a holistic and sustainable development approach.
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 (MGNREGA):
This groundbreaking legislation guarantees a hundred days of wage employment in a financial year to adult members of rural households engaged in unskilled manual work. MGNREGA aims to provide economic support and employment opportunities, significantly contributing to poverty alleviation at the grassroots level.
Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SGSY):
Focused on promoting self-employment among rural individuals, SGSY empowers them to generate sustainable livelihoods. Through financial assistance and training, SGSY aims to uplift beneficiaries economically and foster a culture of entrepreneurship in rural areas.
Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana (PMGY):
A comprehensive initiative spanning various sectors such as education, health, sanitation, and rural development, PMGY aims to uplift communities, enhance living standards, and contribute to poverty reduction by addressing multiple dimensions of rural life.
Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana (PMRY):
Dedicated to generating employment opportunities for the youth, especially in the small-scale sector, PMRY provides financial assistance and support to aspiring entrepreneurs. This initiative fosters economic independence and contributes significantly to poverty eradication.
Collectively, these projects underscore the government’s commitment to combating poverty through multifaceted strategies, addressing both immediate needs and long-term development goals.
By implementing targeted interventions, the government aims to create a positive impact on citizens’ lives, fostering sustainable development and inclusivity across the country.
How can the poor be identified?
One of the widely employed methods for estimating poverty in India involves assessing income or consumption levels. If a household’s income or consumption falls below a specified minimum threshold, it is categorized as below the poverty line (BPL).
This approach provides a quantitative measure to identify and quantify the extent of poverty within the population.
Policymakers, researchers, and social organizations often utilize this method to gauge the prevalence and distribution of poverty, enabling targeted interventions and policy initiatives aimed at uplifting economically disadvantaged households.
The Below Poverty Line criterion serves as a foundational tool for crafting poverty alleviation strategies and designing welfare programs to address the specific needs of vulnerable populations.
When determining the poverty line, it’s crucial to consider factors such as an ideal level of nutrition and non-food expenses based on behavioral patterns. Assessing poverty goes beyond income or consumption, requiring a comprehensive understanding of the resources needed for a decent standard of living.
In this context, individuals or households spending below ₹47 a day in urban areas and ₹32 a day in rural areas are considered below the poverty line. This criterion aims to capture not only basic food needs but also the broader range of non-food expenses crucial to an individual’s overall well-being.
Establishing these thresholds is a vital step in identifying and addressing economic vulnerability, allowing policymakers to tailor interventions beyond immediate income concerns and encompass the various aspects of poverty.
How to get the Benefit of Government Scheme?
| Government Scheme in India | Date of Launch/Implementation |
| Agnipath Defence Policy Reform | September 2022 |
| PM Poshan Shakti Nirman Abhiyaan | 2021 |
| Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS) | April 1, 2021 |
| Ayushman Sahakar Scheme | October 19, 2020 |
| Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay SanraksHan Abhiyan (PM AASHA) | September 2018 |
| SATAT Scheme (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation) | October 2018 |
| Mission Sagar | May 2020 |
| NIRVIK Scheme (Niryat Rin Vikas Yojana) | February 1, 2020 |
| SVAMITVA Scheme (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas) | April 24, 2020 |
| National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM) | February 26, 2020 |
| Mission COVID Suraksha | November 29, 2020 |
| DHRUV – PM Innovative Learning Programme | October 10, 2019 |
| SERB-POWER Scheme (Promoting Opportunities for Women in Exploratory Research) | October 29, 2020 |
| One Nation One Ration Card Scheme (ONORCS) | — |
| Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) | June 1, 2020 |
| Mission Karmayogi | September 2, 2020 |
| Sahakar Mitra Scheme | June 12, 2020 |
| Pradhan Mantri Vaya Vandana Yojana | May 4, 2017 |
What initiatives has the Indian government taken to end poverty there?
Government initiatives, such as the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana and Housing for All by 2022, aim to address the housing needs of both rural and urban populations, especially those from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
These schemes play a crucial role in ensuring that individuals and families, particularly those in poverty, have access to affordable and quality housing, contributing to improved living conditions and overall well-being.
In addition to housing-centric initiatives, the government has introduced contemporary programs like Start-Up India and Stand Up India. These forward-looking initiatives seek to empower individuals by fostering entrepreneurship and supporting aspiring entrepreneurs.
For instance, the Start-Up India initiative encourages the creation and growth of innovative start-ups through financial assistance, mentorship, and various incentives. Similarly, Stand Up India focuses on providing financial assistance to women and individuals from marginalized communities, facilitating the establishment of new enterprises.
By promoting self-employment, innovation, and economic independence, these initiatives align with the broader agenda of poverty alleviation and sustainable development.
The focus on creating opportunities for individuals to earn their livelihood underscores the government’s commitment to fostering inclusive growth and empowering citizens to shape their economic destinies.
These multifaceted schemes represent a comprehensive approach to addressing the diverse needs of the population and catalyzing positive socio-economic transformation.
What are the 3 types of poverty?
- Situational poverty.
- Generational poverty.
- Absolute poverty.
- Relative poverty.
- Urban poverty.
- Rural poverty.
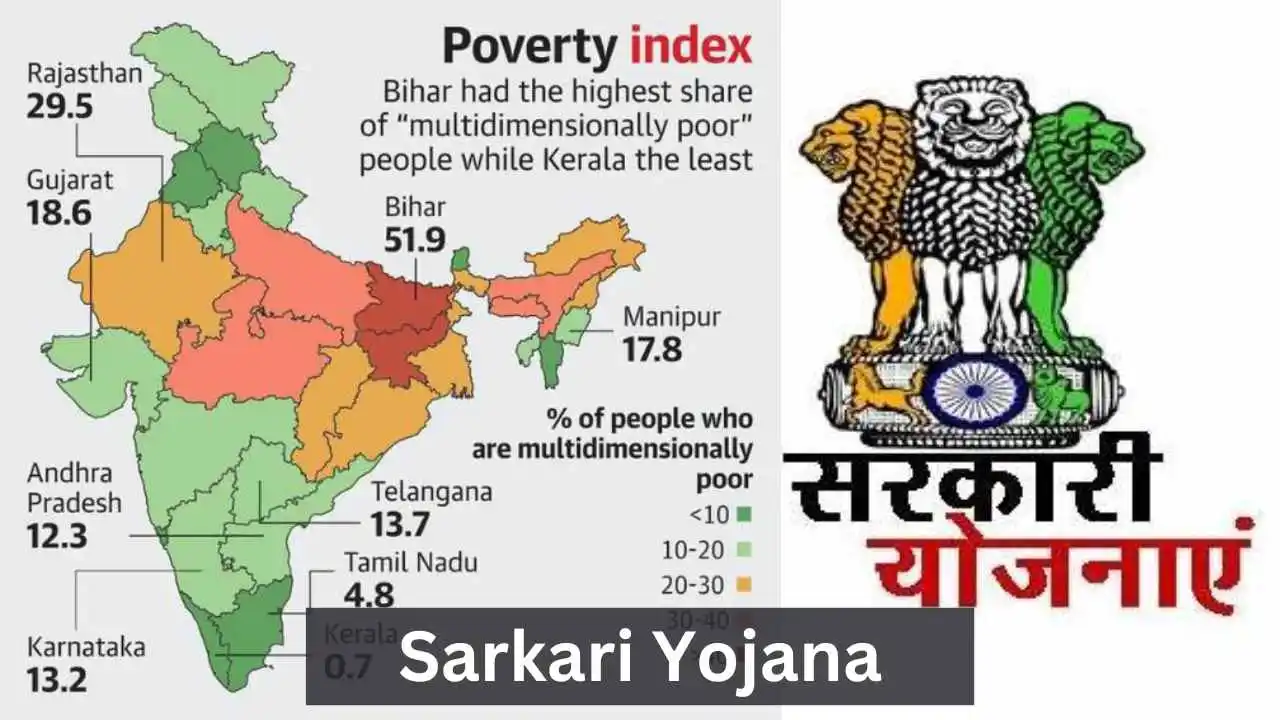
Which is the Poorest state in India?
Bihar, located in eastern India, has long grappled with significant economic challenges, consistently ranking among the country’s poorest states. The state faces a variety of issues contributing to its economic struggles.
Notably, Bihar contends with a high population density, leading to various socio-economic challenges. The implications of a large population are often intertwined with difficulties in resource distribution, employment generation, and overall development.
Moreover, Bihar confronts a concerning low literacy rate, highlighting the need for substantial efforts in educational infrastructure and awareness programs.
Inadequate infrastructure exacerbates these challenges, hindering the state’s ability to provide essential services, connectivity, and a conducive environment for economic growth.
The governance landscape in Bihar has faced scrutiny, with concerns about administrative efficiency and effectiveness. Addressing governance-related issues is crucial for unlocking the state’s potential and fostering sustainable development.
Additionally, limited industrial development poses a hurdle in creating diverse economic opportunities and reducing dependence on traditional sectors.
Navigating these challenges requires strategic interventions, policy reforms, and targeted investments to uplift Bihar’s socio-economic status. Initiatives focusing on education.
Infrastructure development, governance reforms, and industrial growth are imperative to chart a path towards prosperity and address the longstanding economic disparities in Bihar.
- Bihar
- Uttar Pradesh.
- Jharkhand.
- Meghalaya.
- Manipur.
- Assam.
- Madhya Pradesh.
What is India’s rank in poverty?
India’s Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2023 ranking at 111 out of 125 countries raises concerns about the nation’s progress against hunger, showing limited improvement since 2015. Despite this troubling scenario.

The Union government has contested India’s performance for the third consecutive year, citing perceived flaws in the GHI methodology. The government argues that the GHI might not accurately reflect the nuances of India’s initiatives to combat hunger and malnutrition.
This ongoing discrepancy underscores the challenges of measuring and addressing hunger-related issues comprehensively. While the GHI provides valuable insights into critical problems like food insecurity and malnutrition.
Ongoing debates about methodology highlight the need for approaches tailored to India’s context. As the nation confronts these challenges.
There’s a growing consensus on the necessity of collaborative efforts, well-informed policies, and data-driven strategies to make meaningful progress and enhance India’s standing in global hunger indices.
How can poverty be Eradicated?
- improving access to sustainable livelihoods, entrepreneurial opportunities and productive resources;
- providing universal access to basic social services;
- progressively developing social protection systems to support those who cannot support themselves;
- empowering people living in poverty and their organizations;
- addressing the disproportionate impact of poverty on women;
- working with interested donors and recipients to allocate increased shares of ODA to poverty eradication; and
- intensifying international cooperation for poverty eradication.
How many poor people are there in India?
India has significantly reduced multidimensional poverty, witnessing a notable decline of 9.89 percentage points from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-2021.
This positive trend showcases the country’s progress in addressing various dimensions of poverty, with rural areas playing a significant role in this achievement by experiencing the fastest decline from 32.59% to 19.28%.
The effectiveness of targeted policies and interventions aimed at uplifting vulnerable populations is evident in this remarkable improvement.
The decline in multidimensional poverty highlights the positive impact of socio-economic development initiatives, emphasizing the continued importance of efforts to promote inclusive growth and enhance living standards nationwide.
As India continues its developmental journey, maintaining a sustained focus on addressing the diverse facets of poverty remains crucial for achieving comprehensive and lasting positive outcomes.
Conclusion:
Sevak Yojana: Your Go-To Online Free Platform for Connecting and Accessing Comprehensive Information on Sarkari Yojnaa & PM Modi Yojana 2023. Discover the hassle-free process of connecting with and obtaining complete details about government schemes initiated with the support of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chief Ministers on the Sarkari Yojnaa website. Learn about the application procedures with ease!