Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana | UPSC Drishti IAS: On October 11, 2014, Lok Nayak Jai Prakash Narayan’s birthday, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi launched Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) at Vigyan Bhawan in New Delhi. By March 2019, three Adarsh Grams were to be developed, with the first one being completed by 2016. Then, by 2024, five of these Adarsh Grams (one each year) will be chosen and created.

The Scheme, which takes its cues from Mahatma Gandhi’s ideas and values, focuses equal emphasis on fostering national pride, patriotism, community spirit, self-confidence, and infrastructural development. SAGY will preserve the spirit of rural India while giving its residents quality access to essential services and chances to take control of their own lives.
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana | UPSC Drishti IAS
Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) was launched on 11th October 2014 with the aim to translate the comprehensive vision of Mahatma Gandhi about an ideal Indian village into reality, keeping in view the present context. Under SAGY, each Member of Parliament adopts a Gram Panchayat and guides its holistic progress giving importance for social development at par with infrastructure. The ‘Adarsh Grams’ are to become schools of local development and governance, inspiring other Gram Panchayats.
By involving villagers and leveraging scientific tools, a village development plan is prepared under the leadership of Member of Parliament. The distinct feature of this Yojana is that it is:
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Goal
Considering the current situation, Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) aims to establish three Adarsh Grams by March 2019, of which one would be completed by 2016. This comprehensive and organic vision of Mahatma Gandhi is to be translated into reality. Then, by 2024, five of these Adarsh Grams (one each year) will be chosen and created.
Values of Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana
Far beyond mere infrastructure development, SAGY aims at instilling certain values in the villages and their people so that they get transformed into models for others. These values include:
- Adopting people’s participation as an end in itself – ensuring the involvement of all sections of society in all aspects related to the life of village, especially in decision- making related to governance
- Adhering to Antyodaya – enabling the “poorest and the weakest person” in the village to achieve well being
- Affirming gender equality and ensuring respect for women
- Guaranteeing social justice
- Instilling dignity of labour and the spirit of community service and voluntarism
- Promoting a culture of cleanliness
- Living in consonance with nature – ensuring a balance between development and ecology
- Preserving and promoting local cultural heritage
- Inculcating mutual cooperation, self-help and self-reliance
- Fostering peace and harmony in the village community
- Bringing about transparency, accountability and probity in public life
- Nurturing local self-governance
- Adhering to the values enshrined in the Fundamental Rights and Fundamental Duties of the Indian Constitution.
Identification of Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana
The fundamental unit would be a Gram Panchayat. In plain areas, there will be 3000-5000 people, but in mountainous, tribal, and tough locations, there would be 1000–3000 people. When this unit size is unavailable, districts may use Gram Panchayats that approximate the desired population size.
The MP would be free to choose an appropriate Gram Panchayat other than his or her own village or that of his or her spouse to be developed as Adarsh Gram.
One Gram Panchayat will be taken up right away, and two others will be brought up a bit later, according to the MP. The Lok Sabha MP must select a Gram Panchayat from inside his or her district, and the Rajya Sabha MP must select a Gram Panchayat from a rural district in the State from which he or she is elected. MPs who have been nominated may select a Gram Panchayat from any rural district in the nation. The MP will choose a Gram Panchayat from a neighbouring rural constituency in cases where there are no Gram Panchayats in the urban area.
Whether or not SAGY activities have already been started in the GP, the Gram Panchayats that were previously chosen by members of Parliament (whose terms have ended due to resignation or other reasons) will remain in that capacity. The newly elected MPs will be able to choose the general practitioner of their choice, and two more will be available by 2019.
The main objective is to create three Adarsh Grams by March 2019, with the first one being completed by 2016. Then, by 2024, five of these Adarsh Grams (one each year) will be chosen and created.
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Objectives
The main objectives of SAGY are:
- To trigger processes which lead to holistic development of the identified Gram Panchayats
- To substantially improve the standard of living and quality of life of all sections of the population through
- Improved basic amenities
- Higher productivity
- Enhanced human development
- Better livelihood opportunities
- Reduced disparities
- Access to rights and entitlements
- Wider social mobilization
- Enriched social capital
- To generate models of local level development and effective local governance which can motivate and inspire neighbouring Gram Panchayats to learn and adapt
- To nurture the identified Adarsh Grams as schools of local development to train other Gram Panchayats.
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Activities
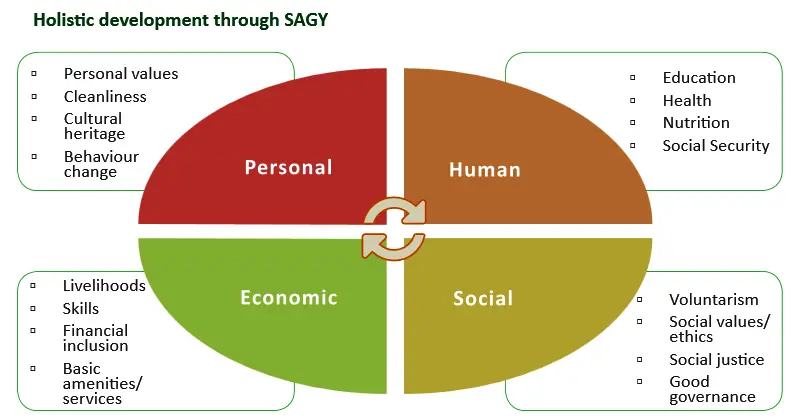
Adarsh Grams should emerge from a community’s common vision, utilizing its members’ skills and resources to the fullest extent while being properly supported by the MP, the Gram Panchayat, civil society, and the political system. Of course, the components of an Adarsh Gram would depend on the situation. The significant activities can still be broadly identified, though. They would consist of:
Personal development:
- Inculcating hygienic behaviour and practices
- Fostering healthy habits including daily exercise and games
- Reducing risk behaviour- alcoholism, smoking, substance abuse, etc.
Human Development:
- Universal access to basic health facilities consisting of health card, medical examination
- Total immunization
- Balancing the sex-ratio
- 100% institutional delivery
- Improving nutrition status for all, with special focus on children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers
- Strong focus on the special needs of Persons with Disability (PWD), especially children and women
- Universal access to education facilities up to Class X and retention
- Conversion of schools into ‘smart schools’. Smart schools will have IT enabled classrooms, e-libraries, web based teaching and will make all students e-literate required for providing quality education
- Adult literacy
- E-literacy
- Village libraries including e-libraries
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Social Development:
- Activities for promotion of voluntarism like Bharat Nirman Volunteers
- Building the capacity of the people to fully participate and contribute to local development
- Activities for honouring village elders, local role models especially women, freedom fighters and martyrs
- Activities for violence and crime free villages such as:
- Setting up Citizen Committees
- Sensitization, especially of youth
- Village sports and folk arts festivals
- Having a village song to instil a sense of pride among the people
- Celebrating ‘Village Day’
- Proactive steps for inclusion and integration of socially excluded groups, especially Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Economic Development:
Promoting diversified agricultural and allied livelihoods, including livestock and horticulture, through-
- Organic farming
- Soil health cards
- Crop intensification such as SRI
- Setting up of seed banks
- Collection and value addition to Non Timber Forest Produce, Livestock development including Gobar Bank, cattle hostel
- Livestock development including Gobar Bank, cattle hostel
- Micro-irrigation
- Agro-service centres
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Rural industrialization like:
Development of skills for all young people who qualify for self-employment and placement
Ecotourism is a subset of village tourism.
All of the aforementioned initiatives should be geared at helping families escape poverty, which makes it crucial to organize and federate women’s SHGs, hire all employees, and promote financial inclusion.
- Post-harvest technology applications
- Micro-enterprises
- Dairy development and processing
- Food processing
- Traditional Industries
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Environmental Development:
- Activities for a clean and green village consisting of:
- Providing toilets in each household and in all public institutions and ensuring their proper use
- Appropriate solid and liquid waste management
- Roadside plantations
- Tree plantation in accordance with local preferences in homesteads, schools and public institutions – including green walkways
- Social forestry
- Watershed management especially renovation and revival of traditional water bodies
- Rainwater harvesting- rooftop as well as others
- Reducing local pollution of air, water and land
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Social Security:
- Pensions for all eligible families- old age, disability and widow
- Insurance schemes like Aam Aadmi Bima Yojana
- Health insurance- RSBY
- PDS- universal access to all eligible households
Basic Amenities and Services:
- Pucca houses for all houseless poor/poor living in kutcha houses
- Drinking water, preferably treated piped water with household taps
- Internal all weather roads with covered drains
- All weather road connectivity to the main road-network
- Electricity connection to all households and street-lights including from alternative sources of energy, especially solar
- Pucca infrastructure for public institutions- Anganwadis, schools, health institutions, Gram Panchayat Office and libraries
- Civic infrastructure including community halls, buildings for SHG federations, playgrounds and burial grounds/ crematoria
- Village markets
- Infrastructure for PDS outlets
- Micro mini banks /post offices/ATMs
- Broadband connectivity and Common Service Centres
- Telecom connectivity
- CCTVs in public places
Benefits and Features of Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana
- This scheme was launched by the Government of India in the year 2014.
- Through this scheme, some Gram Panchayats were identified which would be holistically developed by the Government.
- The development of these Gram Panchayats will be done by the MP by identifying at least 1 village of his constituency.
- MPs of both houses will be motivated to participate under this scheme.
- The benefit of Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana will be provided to more than 2500 villages by the government.
- Through this scheme, the standard of living of citizens living in rural areas will improve.
- Apart from this, they will also become strong and self-reliant.
- Holistic development of identified Gram Panchayats will be done through Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana 2023.
- Apart from this, basic facilities will also be improved.
- The model of rural areas identified by the government under this scheme will be developed in such a way that the surrounding panchayats are inspired and encouraged to learn and adopt those models.
Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana Under Area
Individual:
- Personal moral values
- Cleanliness
- Cultural Heritage
- Changes in behavior
Economic:
- means of livelihood
- skill
- Financial Inclusion
- Infrastructure/Services
Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (FAQ’s)
Q. When was Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana launched?
On October 11th, 2014, the Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) was introduced. The objective was to depict Mahatma Gandhi’s larger vision of an ideal Indian village in a manner consistent with the current situation.
Q. What is Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana?
On October 11th, 2014, the Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) was introduced. The objective was to depict Mahatma Gandhi’s larger vision of an ideal Indian village in a manner consistent with the current situation.
Q. Which Union Ministry implements Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana?
Ministry of Rural Development, Government of India.
Q. Which are the four restrictions in Adarsh Gram Yojana?
Vasectomy (family planning), Kurhad bandi (ban on deforestation), grazing bandi (ban on free grazing), and drug prohibition (ban on alcohol) were the four limitations or “bandis” that the Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana imposed.
Conclusion:
If you’ve any thoughts on the Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana | UPSC Drishti IAS (2023) then feel free to drop them in the below comment box. Keep visiting our website: sevakyojana.com for new updates.
I hope you like this post so please share it on your social media handles & Friends. Don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter to get new updates related to the posts, Thanks for reading this article till the end.
